Creating a Test Plan - CE 5G
Basic Settings:
RLAN
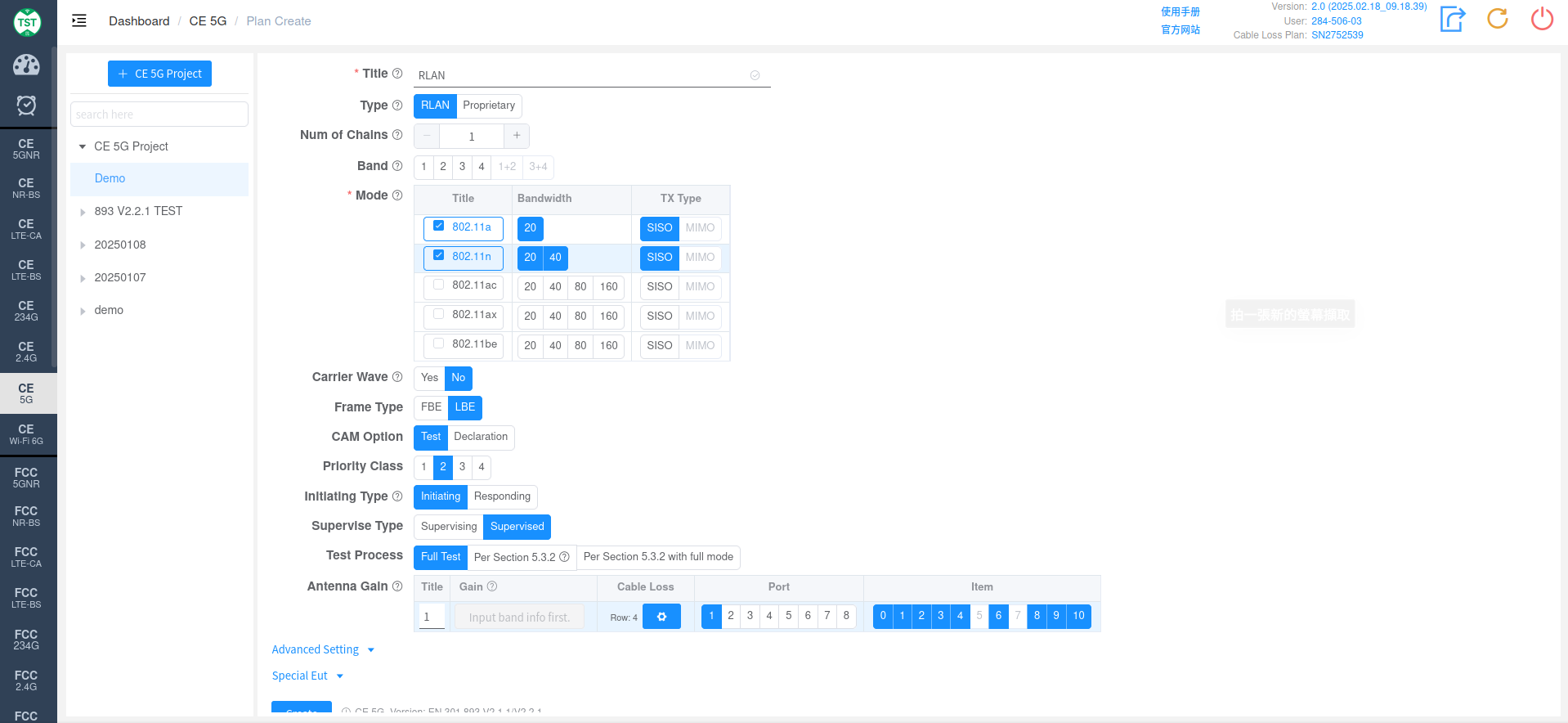
Type: Technical Category, RLAN
Num of Chains: Number of transmit chains (antennas) the product has.
Beamforming: For multi-antenna products, it is also necessary to consider whether the product supports Beamforming.
Beamforming Gain: For products that support beamforming, the additional gain generated by the beamforming technology needs to be filled in.
Band: Operating frequency bands supported by the product. Band 1+2 refers to the entire frequency range of 5150 ~ 5350MHz. If the product supports 160MHz bandwidth, when the channel is 5250MHz, it will cross Band 1 and 2 simultaneously, which is what is referred to as Band 1+2 here. If the product does not support 160MHz bandwidth, there is no need to select Band 1+2.
Mode: Modes and bandwidths supported by the product, as well as TX Type (SISO / MIMO / SISO+MIMO) in multi-antenna scenarios.
RU Config: RU configuration supported by 802.11ax devices.
Beamforming: For multi-antenna products, it is also necessary to consider whether the product supports Beamforming.
Beamforming Gain: For products that support beamforming, the additional gain generated by the beamforming technology needs to be filled in.
Carrier Wave: Whether the product supports carrier wave transmission. If Yes is selected, the frequency error will be measured using carrier mode, and the test setup will be significantly different from modulated signal testing.
TPC Support: Confirm whether the product supports TPC (Transmit Power Control, a mechanism that can automatically adjust the transmit power of the product). This option will affect the Power and PSD limits.
Frame Type: Frame structure of the transmitted signal.
FBE (Frame Based Equipment): Products based on a fixed frame structure. The transmission/reception of such products is periodic, and the period is equal to the fixed frame period. FBE devices can change their fixed frame period, but the time interval cannot be less than 200ms.
LBE (Load Based Equipment): Products whose frame structure changes according to the load type, i.e., the signal transmitted by the product dynamically changes the frame interface according to the amount of data to be transmitted and the number of connected users. RLAN usually belongs to LBE. This option will affect the adaptive test settings. In addition, only LBE categories need to perform CAM (Channel Access Mechanism) channel access technology testing, mainly the Idle Period probability test.
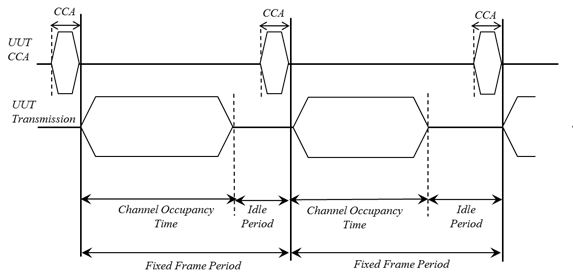
CAM option: Channel Access Mechanism. Confirm whether to perform CAM testing (mainly the Idle Period probability test). For CAM, there are two ways in the regulations to confirm product compliance: option A: measure the probability of the idle period to verify CAM compliance; and option B: declare CAM compliance by describing the product's technical characteristics. Therefore, you can choose whether to test or declare based on the actual situation.
Priority Class: Priority level. If CAM testing is selected, the priority level needs to be selected, with level 2 as the default. Generally speaking, a product may support multiple priorities. According to the description in EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 77, if the priorities supported by the product include 2, CAM is evaluated according to priority 2; otherwise, if the priorities supported by the product include 1, CAM is evaluated according to priority 1; otherwise, if the priorities supported by the product include 3, CAM is evaluated according to priority 3; otherwise, it is evaluated according to priority 4. Different priority evaluation levels will affect the evaluation results of idle period probability.
Initiating Type: Confirm whether the product is an initiating or responding device.
The two main tasks of an initiating device are:
Initialize the communication link and perform channel availability detection.
Coordinate and control the communication requests of responding devices (issue communication permits).
Responding device: Can only transmit signals after receiving permission from the initiating device.
Supervise Type: Confirm whether the product is a supervise or supervised device. This concept is introduced in the Adaptivity test of LBE. The differences between the two are mainly reflected in two aspects: first, the difference in working parameters in EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 30 Table 7 and Table 8; second, the calculation of the idle period probability result is different.
Supervise device: Refers to a device that can control (non-DFS related) working parameters (EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 30 Table 7) during communication.
Supervised device: Non-supervise devices belong to supervised devices.
DFS Type: DFS type of the product, e.g., Master - active listening device, Slave without Radar Detection - slave device without radar detection, etc.
Test Process: Select the test process.
Full Test: The software iterates through all selected modes, bandwidths, and items for testing (large amount of testing).
Per Section 5.3.2: Select the corresponding modes and bandwidths for testing according to EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Section 5.3.2 (testing amount is about one-third of Full Test).
Antenna Gain:
Title: Antenna number, named sequentially by default as 1, 2, 3, 4..., or manually input other names according to customer requirements.
Gain: Gain of each antenna in the corresponding frequency band.
Cable Loss: Cable loss of the RF cable from the product's antenna port to the Switch Box (RF port of the switch) or SA (Spectrum Analyzer, if not using a switch directly). How to Create Common Cable Loss.
Port: Port number of the switch connected to the product's antenna, e.g., Ant1 connected to port 1, Ant2 connected to port 2.
Item: List of all test items included in this standard. *For known product types such as WIFI, Bluetooth, BLE, Zigbee, etc., the software has selected the default required test items based on their respective technical characteristics. Of course, you can also select some items for testing according to your testing needs. Note: In some standards, test parameters are mutually referenced between items. If only some items are checked, the test may not be able to proceed. Therefore, it is recommended to create a test plan using the default items directly. For multi-antenna products, to reduce workload, the first antenna will by default perform tests for all applicable items. However, other antennas have had some mandatory test items selected according to standard requirements. For non-mandatory items, you can check them yourself as needed.
Proprietary
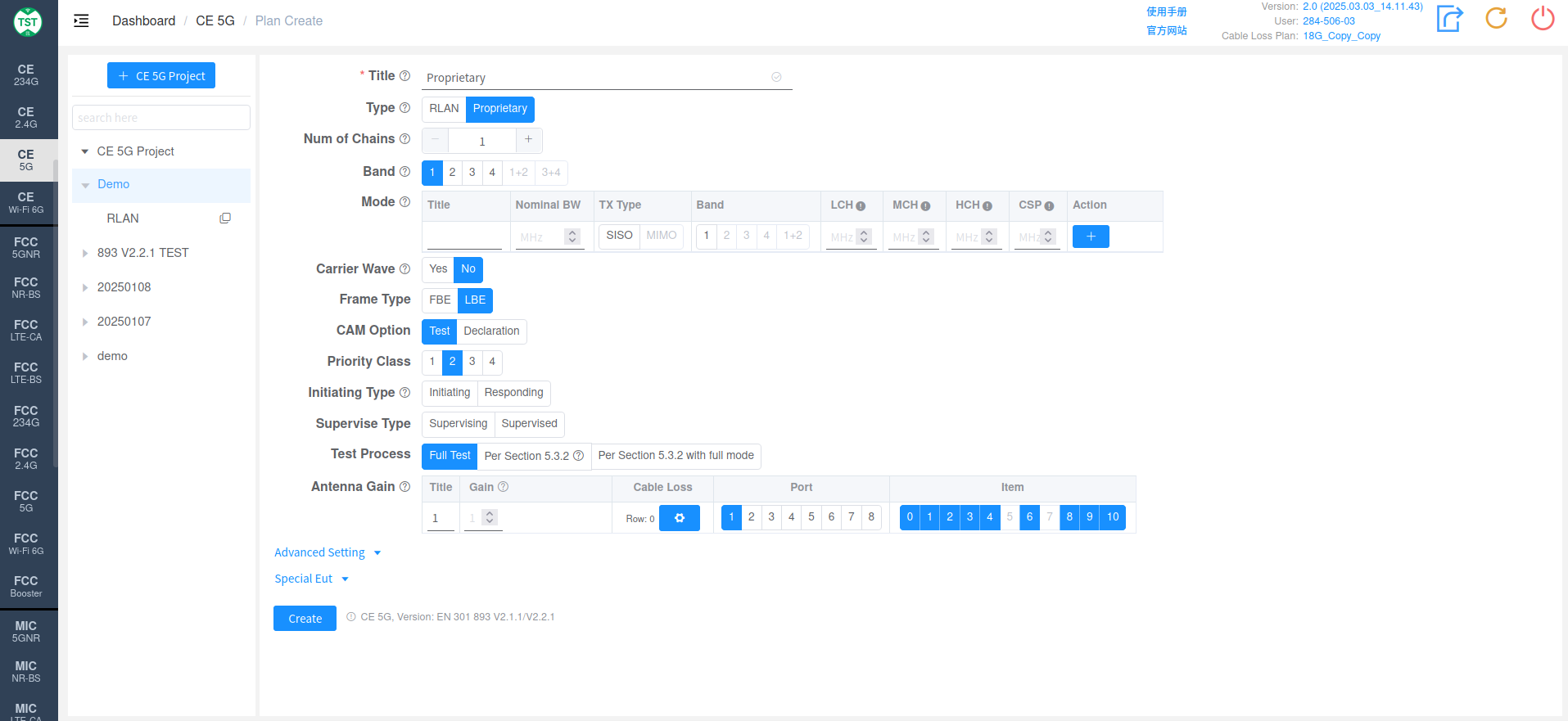
Type: Technical Category, Proprietary
Num of Chains: Number of transmit chains (antennas) the product has.
Beamforming: For multi-antenna products, it is also necessary to consider whether the product supports Beamforming.
Beamforming Gain: For products that support beamforming, the additional gain generated by the beamforming technology needs to be filled in.
Band: Operating frequency bands supported by the product. Band 1+2 refers to the entire frequency range of 5150 ~ 5350MHz. If the product supports 160MHz bandwidth, when the channel is 5250MHz, it will cross Band 1 and 2 simultaneously, which is what is referred to as Band 1+2 here. If the product does not support 160MHz bandwidth, there is no need to select Band 1+2.
Mode:
Title: Mode number, manually input other names according to customer requirements.
Nominal BW: Set the predetermined bandwidth occupied by the signal on the spectrum.
TX Type: Set the transmission type.
SISO: Single Input Single Output. A basic wireless communication transmission method that uses a single antenna for transmitting and receiving.
MIMO: Multiple Input Multiple Output. This transmission method uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive data simultaneously, which can improve communication capacity and reliability.
LCH: Low Channel setting, used to specify the lowest frequency at which communication begins, in MHz.
MCH: Middle Channel setting, used to specify the center frequency of communication.
HCH: High Channel setting, used to specify the highest frequency of communication.
CSP: Channel Spacing, defines the frequency distance between channels. This is very important for broadband communication or devices where multiple channels operate simultaneously.
Action: Used to add new mode configurations.
Carrier Wave: Whether the product supports carrier wave transmission. If Yes is selected, the frequency error will be measured using carrier mode, and the test setup will be significantly different from modulated signal testing.
Frame Type: Frame structure of the transmitted signal.
FBE (Frame Based Equipment): Products based on a fixed frame structure. The transmission/reception of such products is periodic, and the period is equal to the fixed frame period. FBE devices can change their fixed frame period, but the time interval cannot be less than 200ms.
LBE (Load Based Equipment): Products whose frame structure changes according to the load type, i.e., the signal transmitted by the product dynamically changes the frame interface according to the amount of data to be transmitted and the number of connected users. RLAN usually belongs to LBE. This option will affect the adaptive test settings. In addition, only LBE categories need to perform CAM (Channel Access Mechanism) channel access technology testing, mainly the Idle Period probability test.

CAM option: Channel Access Mechanism. Confirm whether to perform CAM testing (mainly the Idle Period probability test). For CAM, there are two ways in the regulations to confirm product compliance: option A: measure the probability of the idle period to verify CAM compliance; and option B: declare CAM compliance by describing the product's technical characteristics. Therefore, you can choose whether to test or declare based on the actual situation.
Priority Class: Priority level. If CAM testing is selected, the priority level needs to be selected, with level 2 as the default. Generally speaking, a product may support multiple priorities. According to the description in EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 77, if the priorities supported by the product include 2, CAM is evaluated according to priority 2; otherwise, if the priorities supported by the product include 1, CAM is evaluated according to priority 1; otherwise, if the priorities supported by the product include 3, CAM is evaluated according to priority 3; otherwise, it is evaluated according to priority 4. Different priority evaluation levels will affect the evaluation results of idle period probability.
Initiating Type: Confirm whether the product is an initiating or responding device.
The two main tasks of an initiating device are:
Initialize the communication link and perform channel availability detection.
Coordinate and control the communication requests of responding devices (issue communication permits).
Responding device: Can only transmit signals after receiving permission from the initiating device.
Supervise Type: Confirm whether the product is a supervise or supervised device. This concept is introduced in the Adaptivity test of LBE. The differences between the two are mainly reflected in two aspects: first, the difference in working parameters in EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 30 Table 7 and Table 8; second, the calculation of the idle period probability result is different.
Supervise device: Refers to a device that can control (non-DFS related) working parameters (EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Page 30 Table 7) during communication.
Supervised device: Non-supervise devices belong to supervised devices.
Test Process: Select the test process.
Full Test: The software iterates through all selected modes, bandwidths, and items for testing (large amount of testing).
Per Section 5.3.2: Select the corresponding modes and bandwidths for testing according to EN 301 893 V2.1.1 (2017-05) Section 5.3.2 (testing amount is about one-third of Full Test).
Antenna Gain:
Title: Antenna number, named sequentially by default as 1, 2, 3, 4..., or manually input other names according to customer requirements.
Gain: Gain of each antenna in the corresponding frequency band.
Cable Loss: Cable loss of the RF cable from the product's antenna port to the Switch Box (RF port of the switch) or SA (Spectrum Analyzer, if not using a switch directly). How to Create Common Cable Loss.
Port: Port number of the switch connected to the product's antenna, e.g., Ant1 connected to port 1, Ant2 connected to port 2.
Item: List of all test items included in this standard. *For known product types such as WIFI, Bluetooth, BLE, Zigbee, etc., the software has selected the default required test items based on their respective technical characteristics. Of course, you can also select some items for testing according to your testing needs. Note: In some standards, test parameters are mutually referenced between items. If only some items are checked, the test may not be able to proceed. Therefore, it is recommended to create a test plan using the default items directly. For multi-antenna products, to reduce workload, the first antenna will by default perform tests for all applicable items. However, other antennas have had some mandatory test items selected according to standard requirements. For non-mandatory items, you can check them yourself as needed.
Advanced Setting and Special Eut Settings:
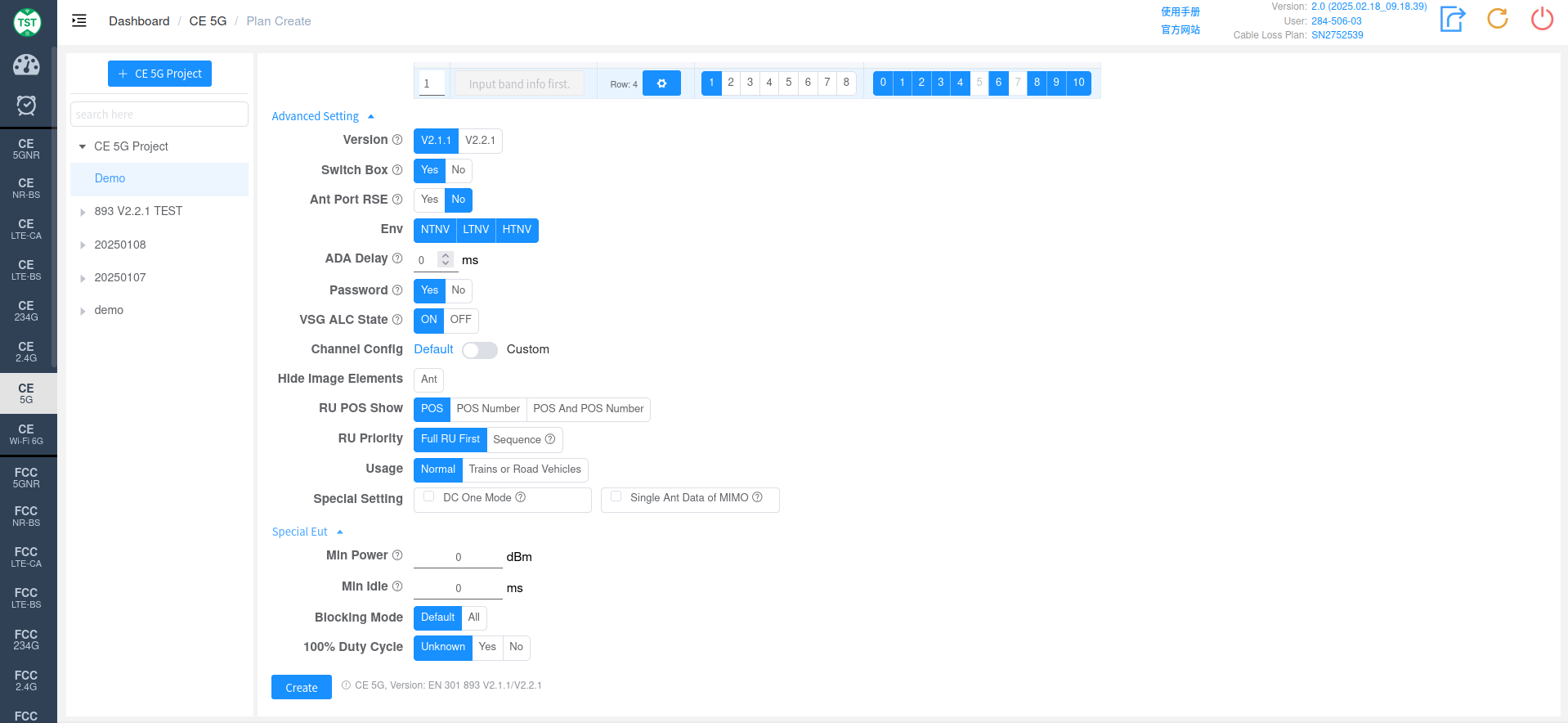
Version: Select the version number. Click the hyperlink in the question mark to set the overall Version of the system.
Switch Box: Whether to use a Switch Box. If a Switch Box has not been purchased, select No for this item, and the product will be directly connected to the spectrum analyzer for testing.
Ant Port RSE: Whether to perform antenna port spurious emissions testing. What is Antenna Port Spurious Emissions Testing.
External Filter: Whether an external filter will be used during antenna port spurious emissions testing.
ENV: Required environmental conditions for testing. e.g., NTNV, LTNV, HTNV (Normal Temperature Normal Voltage, Low Temperature Normal Voltage, High Temperature Normal Voltage).
ADA Delay: Used to simulate network communication delay. By artificially introducing delay, the device's handling of delay in a real network is tested. Click the hyperlink in the question mark to set the overall ADA Delay of the system.
VSG ALC State: Vector Signal Generator power ALC state, used for adaptive testing.
Channel Config: Vector Signal Generator power ALC state, used for adaptive testing.
Config: Check Custom to select Config and manually configure the channel.
Hide Image Elements: Select the image elements to hide.
RU POS Show: Select to display RU POS or RU POS Number or display both together.
RU Priority: RU priority selection, Full RU priority or according to Sequence.
Usage: The power limits are different for the two scenarios. Select the common working environment or the scenario used on trains or cars.
Special Setting: Special settings.
DC One Mode: Only test one duty cycle for one mode, e.g., for 802.11b, only measure the duty cycle of LCH.
Single Ant Data of MIMO: Display EIRP and PSD data of each antenna in MIMO (CE 2.4G/5G/6G).
Min Power: Set the minimum power; 0 represents automatic.
Min Idle: For C2401/C5003, set the minimum Idle.
Blocking Mode: According to regulations, only test the mode with the lowest rate (e.g., only test b mode for b/g/n); All: test all modes.
